Medical Billing: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Information for each patient encounter is used for medical billing. The DX (condition of the patient) and CPT (service rendered to the patient) are used when generating proper medical codes for billing. ICD-10 and CPT codes can easily be extracted from the patient encounter and entered into an invoice used for medical billing. The coding information is used to generate HCFA 1500 (CMS 1500) forms for insurance submission or the information can be submitted electronically through EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) to a medical billing clearinghouse. WebShuttle will guide you through the medical billing process with tools and reminders that make it easy. | Information for each patient encounter is used for medical billing. The DX (condition of the patient) and CPT (service rendered to the patient) are used when generating proper medical codes for billing. ICD-10 and CPT codes can easily be extracted from the patient encounter and entered into an invoice used for medical billing. The coding information is used to generate HCFA 1500 (CMS 1500) forms for insurance submission or the information can be submitted electronically through EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) to a medical billing clearinghouse. WebShuttle will guide you through the medical billing process with tools and reminders that make it easy. | ||
Medical billing is a crucial process in healthcare, ensuring that healthcare providers are reimbursed for their services. The following guide outlines the key steps involved in medical billing, from patient encounters to insurance verification and claims submission. | |||
==Patient Encounters== | |||
During a patient encounter, whether it's an office visit or a telemedicine call, the provider documents the details of the patient's condition and the services rendered in the EHR (Electronic Health Record) system. This includes: | |||
* '''Recording Condition and Services''': Detailed documentation of the patient's condition and services provided. | |||
* '''Transcription''': Audio or video from the encounter is sent for transcription. Transcriptionists convert this into standard documents (e.g., History and Physical, Consultation, Operative Report). | |||
* '''Documentation''': Transcribed documents are attached to the patient chart in the EHR system, capturing the complete condition of the health record. | |||
==Insurance Verification== | ==Insurance Verification== | ||
Verifying patient insurance information is essential to ensure eligibility and policy benefits are documented. This step includes: | |||
* '''Eligibility Check''': Confirming that the patient’s insurance is valid and active. | |||
* '''Policy Benefits''': Understanding the coverage details, co-pays, deductibles, and out-of-pocket expenses. | |||
* '''Prior Authorization''': Obtaining necessary authorizations from the insurance company for certain procedures or treatments. | |||
[[File:Insurance_verification.png|800px]] | |||
[[File: | |||
==Medical Coding== | ==Medical Coding== | ||
Medical coding involves extracting codes from transcribed information to represent the patient's condition and services rendered. This process includes: | |||
* '''ICD-10 and CPT Codes''': Using standardized codes to describe the patient's condition (DX) and services rendered (CPT). | |||
Medical codes | * '''Coder Expertise''': Experienced medical coders review and assign appropriate codes to ensure accuracy. | ||
==Entering Medical Charges== | ==Entering Medical Charges== | ||
Charges for services rendered are entered into the patient invoice. This involves: | |||
* '''Assigning Values''': Each service is assigned a specific charge based on standardized rates. | |||
Charges for services rendered | * '''Invoice Creation''': The billing sheet is prepared, ensuring it is complete and error-free. | ||
==Charge Transmission== | ==Charge Transmission== | ||
Submitting claims to the insurance company is a critical step, known as charge transmission. This can be done electronically through EDI (Electronic Data Interchange). Key points include: | |||
* '''EDI Submission''': Secure and encrypted electronic submission of claims. | |||
* '''Error Checking''': Ensuring all mandatory fields are correctly filled to prevent claim rejections. | |||
[[File:Charge_transmission.png|800px]] | |||
==Denial Management== | ==Denial Management== | ||
Handling denied claims involves: | |||
* '''Follow-Up''': Timely follow-up on denied claims to correct issues and increase the chances of payment. | |||
* '''Evaluation''': Understanding the reasons for denials and taking corrective actions to prevent future issues. | |||
* '''Prioritization''': Focusing on high-priority denials by payer and amount to maximize reimbursements. | |||
==Posting Payments== | ==Posting Payments== | ||
Once payments are received, they need to be posted in the EHR system. This includes: | |||
* '''EOB and ERA''': Processing Explanation of Benefits and Electronic Remittance Advice from insurance companies. | |||
* '''Payment Posting''': Applying the correct payment amounts to each invoice from bulk payments. | |||
==Example Screenshots== | |||
===Invoice List=== | |||
[[File:Invoice_list.png|800px]] | |||
The invoice list shows detailed information about each patient encounter, including encounter ID, date, patient name, code text, claim status, number of items, total charges, payments, and amount due. | |||
===Apply Payment=== | |||
[[File:Apply_payment.png|800px]] | |||
The apply payment screen allows administrators to enter payment details, including check/ref number, check date, deposit date, payment type, payer, and payment amount. | |||
By following these steps, the medical billing process can be streamlined and efficient, ensuring accurate and timely reimbursements for healthcare services provided. | |||
Revision as of 16:52, 22 July 2024
Information for each patient encounter is used for medical billing. The DX (condition of the patient) and CPT (service rendered to the patient) are used when generating proper medical codes for billing. ICD-10 and CPT codes can easily be extracted from the patient encounter and entered into an invoice used for medical billing. The coding information is used to generate HCFA 1500 (CMS 1500) forms for insurance submission or the information can be submitted electronically through EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) to a medical billing clearinghouse. WebShuttle will guide you through the medical billing process with tools and reminders that make it easy.
Medical billing is a crucial process in healthcare, ensuring that healthcare providers are reimbursed for their services. The following guide outlines the key steps involved in medical billing, from patient encounters to insurance verification and claims submission.
Patient Encounters
During a patient encounter, whether it's an office visit or a telemedicine call, the provider documents the details of the patient's condition and the services rendered in the EHR (Electronic Health Record) system. This includes:
- Recording Condition and Services: Detailed documentation of the patient's condition and services provided.
- Transcription: Audio or video from the encounter is sent for transcription. Transcriptionists convert this into standard documents (e.g., History and Physical, Consultation, Operative Report).
- Documentation: Transcribed documents are attached to the patient chart in the EHR system, capturing the complete condition of the health record.
Insurance Verification
Verifying patient insurance information is essential to ensure eligibility and policy benefits are documented. This step includes:
- Eligibility Check: Confirming that the patient’s insurance is valid and active.
- Policy Benefits: Understanding the coverage details, co-pays, deductibles, and out-of-pocket expenses.
- Prior Authorization: Obtaining necessary authorizations from the insurance company for certain procedures or treatments.
File:Insurance verification.png
Medical Coding
Medical coding involves extracting codes from transcribed information to represent the patient's condition and services rendered. This process includes:
- ICD-10 and CPT Codes: Using standardized codes to describe the patient's condition (DX) and services rendered (CPT).
- Coder Expertise: Experienced medical coders review and assign appropriate codes to ensure accuracy.
Entering Medical Charges
Charges for services rendered are entered into the patient invoice. This involves:
- Assigning Values: Each service is assigned a specific charge based on standardized rates.
- Invoice Creation: The billing sheet is prepared, ensuring it is complete and error-free.
Charge Transmission
Submitting claims to the insurance company is a critical step, known as charge transmission. This can be done electronically through EDI (Electronic Data Interchange). Key points include:
- EDI Submission: Secure and encrypted electronic submission of claims.
- Error Checking: Ensuring all mandatory fields are correctly filled to prevent claim rejections.
Denial Management
Handling denied claims involves:
- Follow-Up: Timely follow-up on denied claims to correct issues and increase the chances of payment.
- Evaluation: Understanding the reasons for denials and taking corrective actions to prevent future issues.
- Prioritization: Focusing on high-priority denials by payer and amount to maximize reimbursements.
Posting Payments
Once payments are received, they need to be posted in the EHR system. This includes:
- EOB and ERA: Processing Explanation of Benefits and Electronic Remittance Advice from insurance companies.
- Payment Posting: Applying the correct payment amounts to each invoice from bulk payments.
Example Screenshots
Invoice List
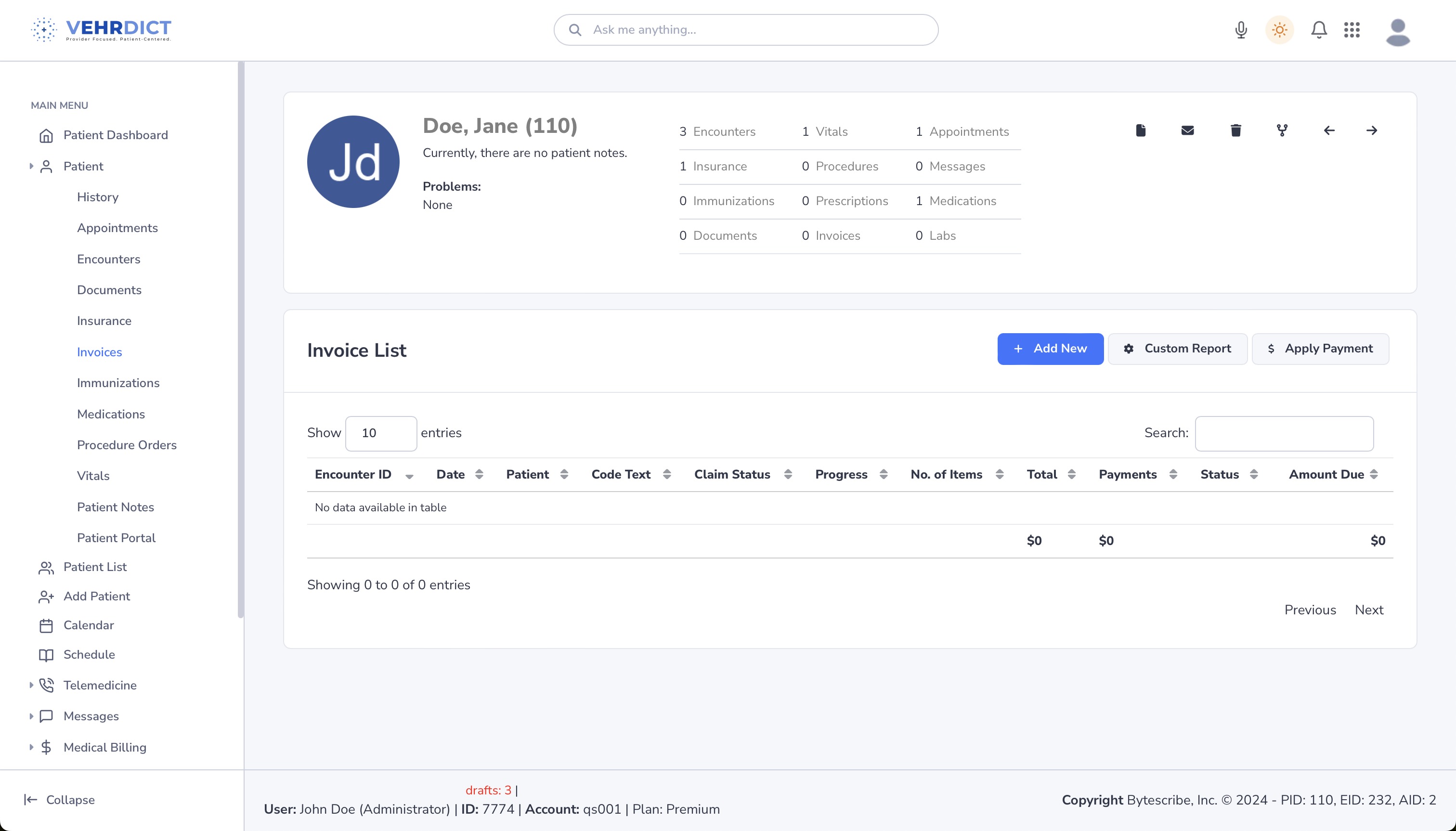 The invoice list shows detailed information about each patient encounter, including encounter ID, date, patient name, code text, claim status, number of items, total charges, payments, and amount due.
The invoice list shows detailed information about each patient encounter, including encounter ID, date, patient name, code text, claim status, number of items, total charges, payments, and amount due.
Apply Payment
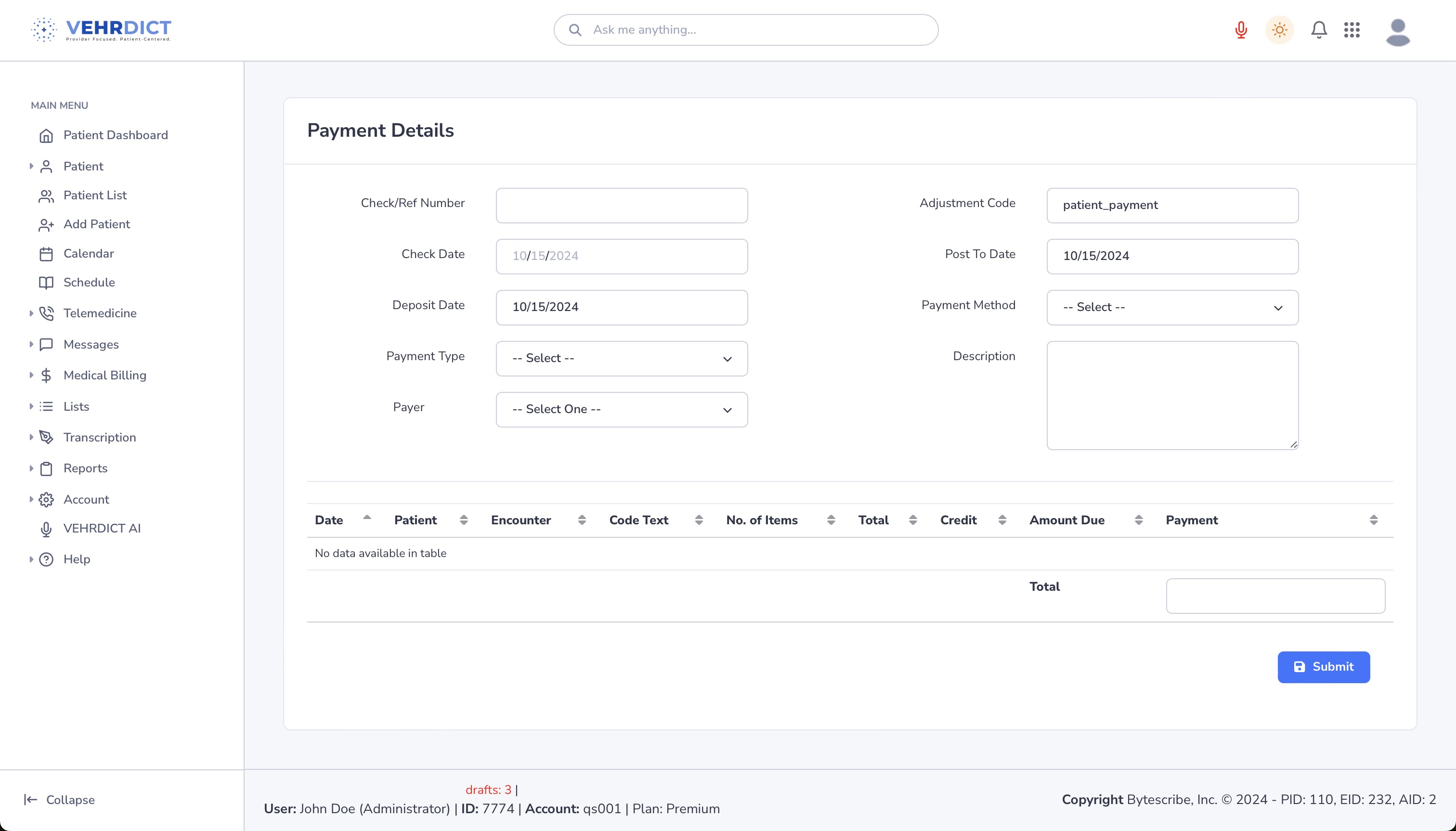 The apply payment screen allows administrators to enter payment details, including check/ref number, check date, deposit date, payment type, payer, and payment amount.
The apply payment screen allows administrators to enter payment details, including check/ref number, check date, deposit date, payment type, payer, and payment amount.
By following these steps, the medical billing process can be streamlined and efficient, ensuring accurate and timely reimbursements for healthcare services provided.