Medical Billing: Difference between revisions
Created page with "Information for each patient encounter is used for medical billing. The DX (condition of the patient) and CPT (service rendered to the patient) are used when generating proper medical codes for billing. ICD-10 and CPT codes can easily be extracted from the patient encounter and entered into an invoice used for medical billing. The coding information is used to generate HCFA 1500 (CMS 1500) forms for insurance submission or the information can be submitted electronica..." |
No edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The Medical Billing & Claims features in VEHRDICT are built to help your practice manage the entire revenue cycle—from capturing billing codes to tracking payments and resubmitting denied claims. This support page explains how each part of the billing workflow functions in the system, and how you can use VEHRDICT to ensure faster reimbursements and fewer billing errors. | |||
===CPT/ICD code selection and AI extraction=== | |||
When documenting a patient encounter, VEHRDICT automatically scans the clinical notes and suggests appropriate CPT and ICD-10 codes based on the content. These AI-suggested codes appear in the billing section of the encounter for your review. You can accept, remove, or manually add additional codes as needed. If your practice uses a set of common codes frequently, you can mark them as favorites so they are easy to access and reuse for future visits. | |||
===Claim generation and clearinghouse submission=== | |||
Once billing codes and patient insurance information are finalized, VEHRDICT can generate a claim with just a few clicks. The system automatically formats the claim according to ANSI 837P standards and submits it to your connected clearinghouse. You don’t need to export files or handle separate billing software—everything happens directly from within the EHR. Each claim is assigned a tracking ID, and the status is monitored continuously for updates such as accepted, rejected, or paid. | |||
===Eligibility verification=== | |||
Before submitting a claim or even during check-in, VEHRDICT allows you to verify a patient's insurance eligibility in real time. This feature connects to insurance payers electronically and confirms active coverage, plan details, and co-pay information. You can access the verification results from the patient profile or directly from the appointment screen. Verifying eligibility ahead of time helps reduce claim denials and prevents surprises for both the practice and the patient. | |||
== | ===Payment posting=== | ||
When payment information is received from the clearinghouse or entered manually, VEHRDICT makes it easy to post payments to the correct patient account. The system can automatically match Explanation of Benefits (EOB) data with submitted claims, and apply payments, adjustments, or patient balances accordingly. Staff can view posted payments in the billing history section and apply filters to review specific services, dates, or payers. | |||
===Denial management and resubmissions=== | |||
If a claim is denied or returned with errors, VEHRDICT highlights the issue and provides guidance on what needs to be corrected. You can open the claim, make the necessary adjustments, and resubmit it directly through the system without re-entering all the data. All denial reasons and resubmission attempts are logged, allowing your staff to track patterns and reduce repeat issues. This helps ensure quicker resolutions and fewer delays in reimbursement. | |||
===Patient invoicing and receipts=== | |||
VEHRDICT can generate detailed invoices for patient balances, including charges, payments, and adjustments. You can print or email invoices directly from the system, and each invoice includes your practice’s information and payment instructions. When a payment is made, a receipt can be issued immediately. This ensures that patients are well-informed of their financial responsibility and that your practice maintains clear and professional billing records. | |||
== Insurance Verification == | |||
Before billing, it is essential to confirm the patient’s insurance status and understand their benefits. This ensures coverage and reduces claim denials. | |||
* '''Eligibility Check''' – Confirm policy is active | |||
* '''Policy Benefits''' – Review co-pays, deductibles, and coverage limits | |||
* '''Prior Authorization''' – Secure approvals for procedures if required | |||
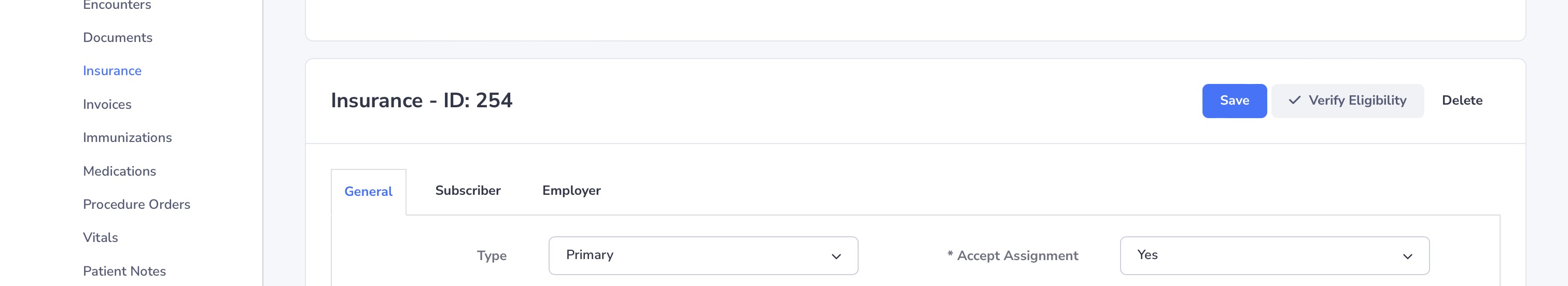
[[File:insurance_eligibility_nx.jpg|800px|'''Insurance Verification Screen''' – Review eligibility, coverage, and authorization status.]] | |||
== Medical Coding == | |||
Once documentation is complete, coders extract: | |||
* '''ICD-10 Codes''' – Patient diagnoses (DX) | |||
* '''CPT Codes''' – Services performed | |||
Accurate coding is vital for correct billing and compliance with insurance regulations. Experienced coders ensure codes reflect the medical necessity and scope of service. | |||
{{Tip|Coding errors are one of the top reasons for claim denials. Always double-check code pairings and modifier usage.}} | |||
== Entering Medical Charges == | |||
Charges are entered into the system based on documented services: | |||
* '''Assigning Charges''' – Each CPT code is linked to a standardized billing rate | |||
* '''Invoice Creation''' – Review for completeness and accuracy before submission | |||
This creates a billing record used for claim generation and submission. | |||
== Charge Transmission == | |||
Sending claims to payers is done via secure EDI (Electronic Data Interchange): | |||
* '''EDI Submission''' – HIPAA-compliant, encrypted claim transmission | |||
* '''Error Checking''' – Automated checks to reduce rejections | |||
'''VEHRDICT''' tools assist in preparing, reviewing, and transmitting claims efficiently. | |||
{{Tip|Use the EDI error checker to catch missing diagnosis codes, date mismatches, or NPI errors before submission.}} | |||
== Denial Management == | |||
[[File:Payment | For denied claims, follow-up is essential: | ||
* '''Tracking and Follow-Up''' – Monitor status and resolve issues | |||
* '''Root Cause Evaluation''' – Identify and address denial reasons | |||
* '''Priority Handling''' – Focus efforts based on claim value and payer | |||
{{Warning|Denials left unresolved can result in significant revenue loss. Implement a daily check of pending/denied claims.}} | |||
== Payment Posting == | |||
Once insurance payments are received: | |||
* '''EOB & ERA Review''' – Cross-reference with expected charges | |||
* '''Apply Payments''' – Match incoming payments with corresponding invoices | |||
Accurate posting ensures financial reporting and patient balance accuracy. | |||
== Example Screenshots == | |||
=== Invoice List === | |||
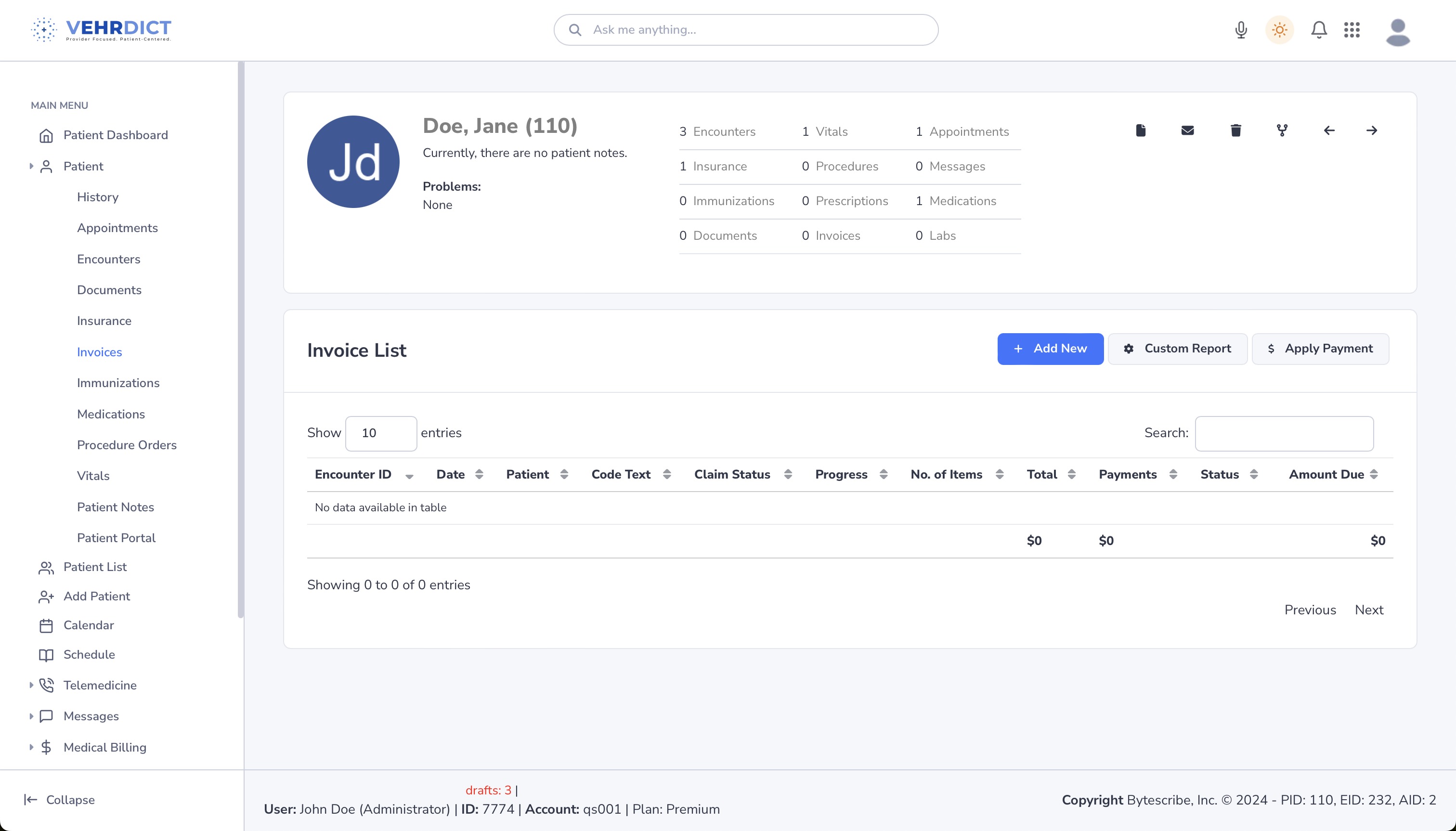
[[File:Invoice_list.png|800px|'''Invoice List''' – View encounters, claim statuses, total charges, payments, and balance due.]] | |||
=== Apply Payment === | |||
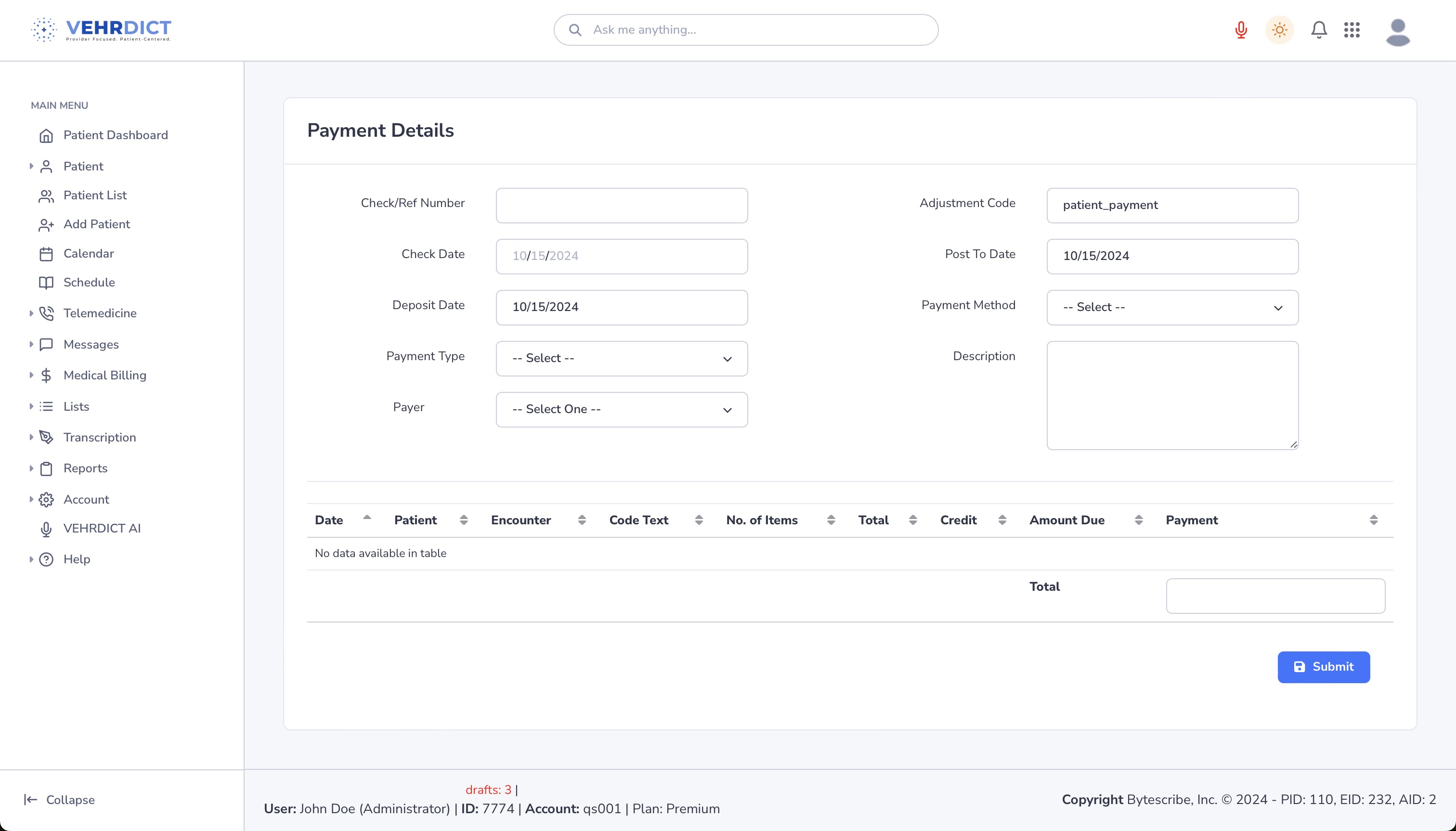
[[File:Apply_payment.png|800px|'''Apply Payment Screen''' – Enter and reconcile payment details from insurance payers.]] | |||
== Summary == | |||
By following these steps in the '''VEHRDICT''' system, your practice can streamline billing workflows, minimize errors, and ensure fast and accurate reimbursements for all patient services. | |||
Latest revision as of 22:22, 15 July 2025
The Medical Billing & Claims features in VEHRDICT are built to help your practice manage the entire revenue cycle—from capturing billing codes to tracking payments and resubmitting denied claims. This support page explains how each part of the billing workflow functions in the system, and how you can use VEHRDICT to ensure faster reimbursements and fewer billing errors.
CPT/ICD code selection and AI extraction
When documenting a patient encounter, VEHRDICT automatically scans the clinical notes and suggests appropriate CPT and ICD-10 codes based on the content. These AI-suggested codes appear in the billing section of the encounter for your review. You can accept, remove, or manually add additional codes as needed. If your practice uses a set of common codes frequently, you can mark them as favorites so they are easy to access and reuse for future visits.
Claim generation and clearinghouse submission
Once billing codes and patient insurance information are finalized, VEHRDICT can generate a claim with just a few clicks. The system automatically formats the claim according to ANSI 837P standards and submits it to your connected clearinghouse. You don’t need to export files or handle separate billing software—everything happens directly from within the EHR. Each claim is assigned a tracking ID, and the status is monitored continuously for updates such as accepted, rejected, or paid.
Eligibility verification
Before submitting a claim or even during check-in, VEHRDICT allows you to verify a patient's insurance eligibility in real time. This feature connects to insurance payers electronically and confirms active coverage, plan details, and co-pay information. You can access the verification results from the patient profile or directly from the appointment screen. Verifying eligibility ahead of time helps reduce claim denials and prevents surprises for both the practice and the patient.
Payment posting
When payment information is received from the clearinghouse or entered manually, VEHRDICT makes it easy to post payments to the correct patient account. The system can automatically match Explanation of Benefits (EOB) data with submitted claims, and apply payments, adjustments, or patient balances accordingly. Staff can view posted payments in the billing history section and apply filters to review specific services, dates, or payers.
Denial management and resubmissions
If a claim is denied or returned with errors, VEHRDICT highlights the issue and provides guidance on what needs to be corrected. You can open the claim, make the necessary adjustments, and resubmit it directly through the system without re-entering all the data. All denial reasons and resubmission attempts are logged, allowing your staff to track patterns and reduce repeat issues. This helps ensure quicker resolutions and fewer delays in reimbursement.
Patient invoicing and receipts
VEHRDICT can generate detailed invoices for patient balances, including charges, payments, and adjustments. You can print or email invoices directly from the system, and each invoice includes your practice’s information and payment instructions. When a payment is made, a receipt can be issued immediately. This ensures that patients are well-informed of their financial responsibility and that your practice maintains clear and professional billing records.
Insurance Verification
Before billing, it is essential to confirm the patient’s insurance status and understand their benefits. This ensures coverage and reduces claim denials.
- Eligibility Check – Confirm policy is active
- Policy Benefits – Review co-pays, deductibles, and coverage limits
- Prior Authorization – Secure approvals for procedures if required
Medical Coding
Once documentation is complete, coders extract:
- ICD-10 Codes – Patient diagnoses (DX)
- CPT Codes – Services performed
Accurate coding is vital for correct billing and compliance with insurance regulations. Experienced coders ensure codes reflect the medical necessity and scope of service.
Tip: Coding errors are one of the top reasons for claim denials. Always double-check code pairings and modifier usage.
Entering Medical Charges
Charges are entered into the system based on documented services:
- Assigning Charges – Each CPT code is linked to a standardized billing rate
- Invoice Creation – Review for completeness and accuracy before submission
This creates a billing record used for claim generation and submission.
Charge Transmission
Sending claims to payers is done via secure EDI (Electronic Data Interchange):
- EDI Submission – HIPAA-compliant, encrypted claim transmission
- Error Checking – Automated checks to reduce rejections
VEHRDICT tools assist in preparing, reviewing, and transmitting claims efficiently.
Tip: Use the EDI error checker to catch missing diagnosis codes, date mismatches, or NPI errors before submission.
Denial Management
For denied claims, follow-up is essential:
- Tracking and Follow-Up – Monitor status and resolve issues
- Root Cause Evaluation – Identify and address denial reasons
- Priority Handling – Focus efforts based on claim value and payer
Warning: Denials left unresolved can result in significant revenue loss. Implement a daily check of pending/denied claims.
Payment Posting
Once insurance payments are received:
- EOB & ERA Review – Cross-reference with expected charges
- Apply Payments – Match incoming payments with corresponding invoices
Accurate posting ensures financial reporting and patient balance accuracy.
Example Screenshots
Invoice List
Apply Payment
Summary
By following these steps in the VEHRDICT system, your practice can streamline billing workflows, minimize errors, and ensure fast and accurate reimbursements for all patient services.